Section-1 Mental Ability Test (MAT)
This is non – verbal test. Questions are based on figures and diagrams
only. Questions are meant to assess general mental functioning of the
candidates. The section is divided into ten paras having 5 questions each.
Given below are some examples:
PART-I ( ODD-MAN
OUT)
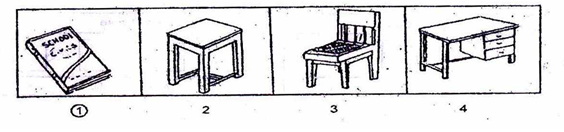
Directions:-In questions 1 to 5, four figures 1, 2, 3 and 4 have been given in each
question. Of these four figures, three figures are similar in some way and one
figure is different. Select the figure which is different.
PART- II ( FIGURE MATCHING)
Directions:
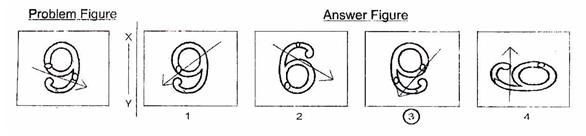
In questions 6 to 10, a problem figure is given on the left side and
four answer figures marked 1, 2, 3, 4 are given on the right side. Select the
answer figure which is exactly the same as the problem figure.
PART- III
( PATTERN COMPLETION)
Directions:
In questions 11 to 15 there is a problem figure on the left hand side, a
part of which is missing. Observe the answer figures 1, 2, 3, 4 on the right
hand side and find out the answer figure which without changing the direction,
fits in the missing part of the problem figure in order to complete the pattern
in the problem figure.
PART- IV
( FIGURE SERIES COMPLETION)
Directions:
In questions 16 to 20, there are three problem figures on the left hand
side and the space for the fourth figure is left blank. The problem figures are
in a series. Find out one figure from among the answer figures given on the
right hand side, which occupies the blank space for the fourth figure on the
left hand side and completes the series.
PART - V
( ANALOGY)
In questions 21 to 25, there are two sets of two problem figures each.
The second set has a mark of interrogation (?). There exists a relationship
between the first two problem figures. Similar relationship should exist
between the third and fourth problem figure. Select one of the answer figure
which replaces the mark of interrogation.
PART - VI { Geometrical Figure Completion (Triangle, Square, Circle) }
Directions:
In questions 26 to 30 one part of a square is on the left hand side as
question figure and the other one is among the four answer figures 1, 2, 3, 4
given on the right hand side. Find out the figure that completes the square.
PART – VII (MIRROR IMAGING)
Directions:
In questions 31 to 35 there is a problem figure on the left side and
four answer figures marked 1, 2, 3, 4 are given on the right side. Select the
answer figure which is exactly the mirror image of the problem figure when the
mirror is held at X Y.
PART - VIII (PUNCHED HOLD PATTERN - Folding/Unfolding)
Directions:
In question 36 to 40 a piece of paper is folded and punched as shown in
problem figures on the left side and four answer figures marked 1, 2, 3, 4 are
given on right side. Select the answer figure which indicates how the paper
will appear when opened (unfolded).
In questions 41 to 45 a problem figure is given on the left side and
four answer figures, marked 1, 2, 3, 4 are given on the right side. Select the
answer figure which can be formed from the cut-off pieces given in the problem
figure. PART –X (EMBEDDED FIGURE)
PART –X (EMBEDDED FIGURE)
 PART –X (EMBEDDED FIGURE)
PART –X (EMBEDDED FIGURE)
Directions:
In
questions 46 to 50 a problem figure is given on the left side and four answer
figures, marked 1, 2, 3, 4 are given on the right side. Select the answer
figure in which the problem figure is hidden/ embedded
Section 2: Arithmetic Test
The main
purpose of this test is to measure candidate's basic competencies in
Arithmetic. All the Twenty-five questions of this test will be based on the
following 15 topics
1.
Number and numeric system.
2.
Four fundamental operations on whole number.
3.
Fractional number and four
fundamental operations on them.
4.
Factors and multiple including
their properties.
5.
LCM and HCF of numbers.
6.
Decimals and fundamental
operations on them.
7.
Conversion of fractions to
decimals and vice-versa.
8.
Applications of number in measure
length, mass, capacity, time, money etc
9.
Distance, time and speed.
10.
Approximation of expressions.
11.
Simplification of Numerical
Expressions,
12.
Percentage and its applications.
13.
Profit and loss.
14.
Simple interest.
15.
Perimeter, area and volume.
Note:- Emphasis will be more on
testing of understanding and Application of the concepts and skills involved.
In order to provide some guidance to the candidates on the types of questions
that are expected in Arithmetic lest, some examples are given below-
Example - 1 (Test of Understanding):
What is
the prime factorization of 1000?
1.
10x10x10
2.
2x5x5x10
3.
2 x 2 x 2
x5 x 5
4.
2 x 2x 2 x 5 x5 x 5
A factorization of a number is said to be a prime factorization if (i)
the product of the factors (taking a factor as many times as it occurs) is
equal to the given number, and (ii) each factor is a prime number. Here only
serial number 4 satisfies both the requirements. As such, serial number 4 is
the correct answer.
Example 2 (Test of Understanding):
What is
the average of first four odd
numbers?
a.
2.5
b. 4
c. 5
d.
16
The first
four odd numbers are 1.3.5 and 7. Their average (l+3+5+7)/4. As such, serial
number 2 is the correct answer.
Example 3 (Test of Application):
A 1 km. long goods train is running at speed of I km. per 3 minutes, the
time taken by this train to pass through 2 kms. Long tunnel is:
1.
1 minute
2.
3 minute
3.
6 minute
4.
9 minute
The tunnel is 2 km. long and the train is I km. in length, the train
will have to cover a total distance of 3
km. in order to pass through the tunnel running at a speed of 1 km, per 3
minutes, the train will take 9 minutes to pass through ibis tunnel and that is
the correct answer. As such, serial number 4 is the correct answer.
Section 3: Language Test.
The main purpose of this test is to assess reading comprehension of the
candidates. The test consists of three passages. Each passage is followed by 5
questions. Candidates shall read each passage carefully and answer the
questions that follow. In addition, there will be 10 questions to test grammar
and writing skills of candidates.
PASSAGE
Forests
are useful to us in many ways. They provide us with timber to build houses and
make furniture. Forests also provide us with wood for fuel and making paper.
They provide shelter for birds, wild animals and insects. Forests bring
rainfall. Existence of forests is very important for the preservation of the
ecosystem. The fact that we have to care for an ecosystem is indisputably
established. Wise use of the environment and its resources are essential for
man's continued survival.
1.
To
preserve the ecosystem, existence of...............is essential.
1.
forests
2.
animals
3.
human beings
4.
resources
2.
Opposite
of preservation' is...............
1.
conservation
2.
construction
3.
shelter
4.
destruction
3.
Which one
of the following is not a synonym of 'wise'?
1.
Sensible
2.
Intelligent
3.
Humorous
4.
Judicious
4.
Carpenters
depend on forests because they provide...............
1.
wood for fuel
2.
wood for making paper
3.
timber to make furniture
4.
houses for animals
5.
Wild animals will become homeless if...............
1.
paper mills are destroyed
2.
houses are built
3.
forests are destroyed
4.
ecosystem is taken care of
OMR Answer Sheet Sample
For more updates visit:- Find us on Facebook









Navodaya Vidyalaya Class 6 Exam 2017 Syllabus, Books | Navodaya Entrance Exam/Test Syllabus, Instructions, Model Papers | JNVST 2018-2019 Exam Pattern| Syllabus and model papers
ReplyDelete